
In this tutorial, you will learn the variable declaration in C language. A variable is an identifier or a name that is used to refer to a value and this value varies or changes during the program execution. A variable is written with a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters or underscores with the first letter being an alphabet. A maximum of 31 letters can be used to write a variable.
Example:-
x, fact, c22, total_values etc.
Also read, Constant in C with example
Consider the below points while variable declaration in C language
- Uppercase and lowercase alphabets are taken differently. For example, the variables ‘SUM’ and ‘sum’ are pointing to different values.
- No special characters other than underscore(_) are permitted.
- Some C compilers will not accept more than 8 characters. So it is better to declare a variable with a few letters that make it easy to use.
- All the variables used in the C program are declared with the appropriate data types before assigning a value to that variable. For eg:- int intNum = 3;
- reserved words can not be used as variables.
Lets us take an example below
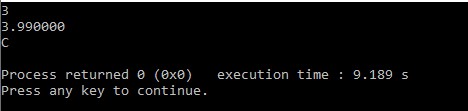
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// Create variables
int intNum = 3; // Integer (whole number)
float floatNum = 3.99; // Floating point number
char letter = 'C'; // Character
// Print variables
printf("%d\n", intNum);
printf("%f\n", floatNum);
printf("%c\n", letter);
return 0;
}
Output:-
Conclusion:- I hope this tutorial will help you to understand the overview of variable declaration. If there is any doubt then please leave a comment below.